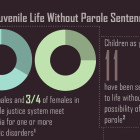
As the U.S. Supreme Court prepares to hear oral arguments in the cases of two 14-year-olds sentenced to spend the rest of their lives in prison, many advocates and attorneys predict a majority of the justices will decide that life sentences for juveniles without the possibility of parole amounts to cruel and unusual punishment. Children are “categorically different” from adults, says Andrea Dennis, associate professor at the University of Georgia School of Law, and she wants to see the Court acknowledge that. “At a minimum,” she said, “I hope the court would reject mandatory juvenile LWOP [life without parole] sentences for all homicide crimes and require juries be allowed to consider the defendant’s youth and other factors as mitigation.”
In both cases, Jackson v. Hobbs and Miller v. Alabama, the sentences were mandatory regardless of the defendant’s age or circumstances and the judges had no discretion in sentencing. In Jackson, a 14-year-old was convicted as an accomplice to the murder of a store clerk. He did not have a gun or pull the trigger.