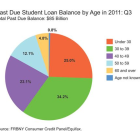
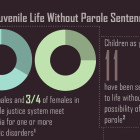
Funding for Juvenile Code is Major Concern as Legislature Winds Down
|
Wildly divergent estimates of the pricetag for Georgia's proposed juvenile code rewrite continue to swirl around the Capitol as lawmakers return for their last three days of 2012. The 246-page bill has cleared the state House and is expected to come before the full Senate this week, possibly Tuesday, with only minor changes. Gov. Nathan Deal's office continues to crunch the numbers to help him decide whether the state budget can absorb the expense. "We have solid support in the General Assembly, and we are hopeful the governor will support it as well," said Kirsten Widner, lobbyist for the Barton Child Law and Policy Center. "If he's not on board, you can't achieve the goals of the legislation."